WHAT IS
Weight Loss Surgery?
Weight loss surgery is a medical procedure designed to help people lose weight when other methods like diet and exercise have not been effective.
Weight loss surgery is also known as Bariatric Surgery. We perform the Sleeve Gastrectomy and the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass for the management of obesity. Both operations are usually performed with laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery.
Each operation comes with different risks, side effects, and benefits. The decision between which operation to perform will be made in conjunction with you and your surgeon, and will depend on individual circumstances.
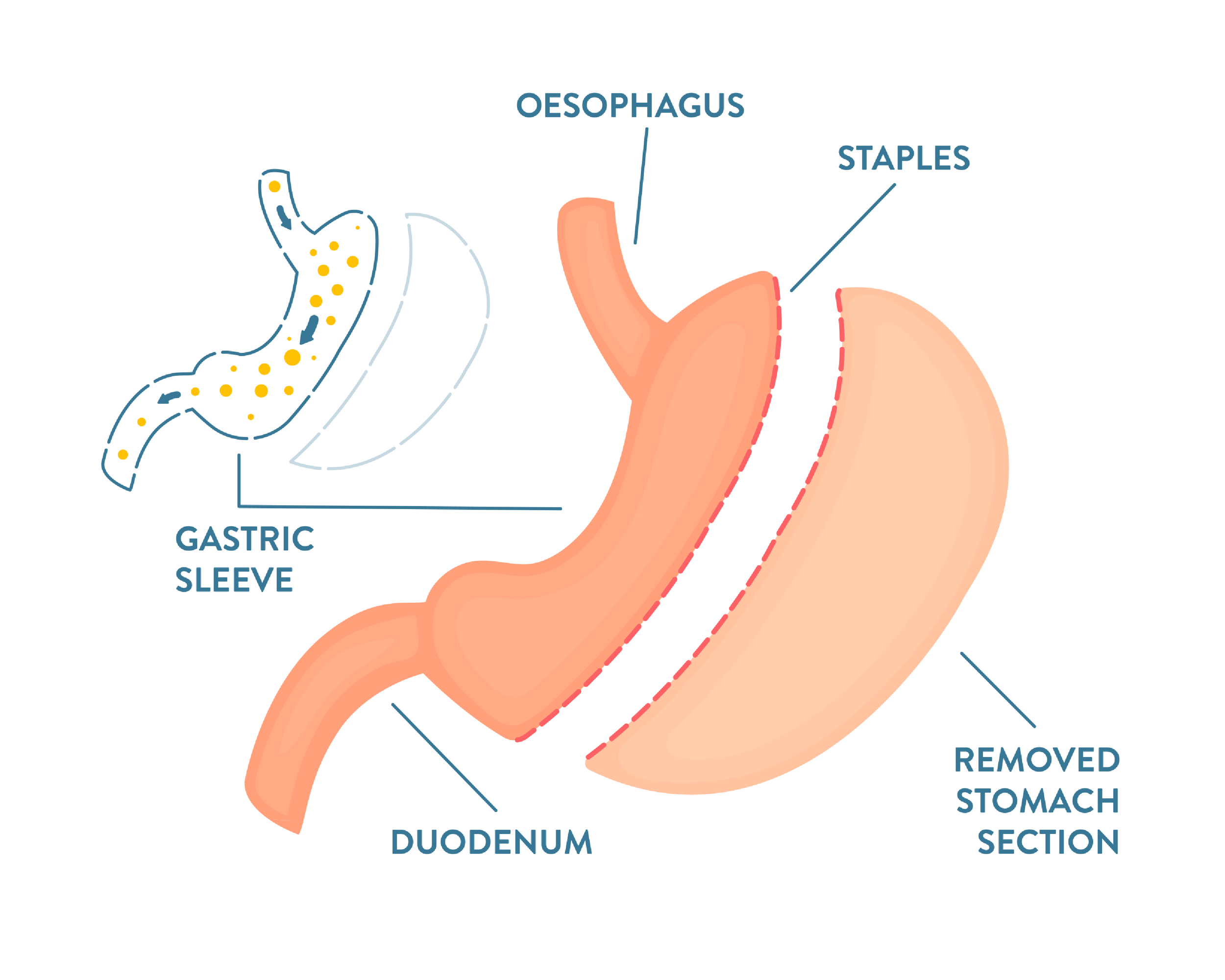
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
With this operation, a large portion of the stomach is removed, leaving a smaller, sleeve-shaped stomach. This reduces the capacity of the stomach, causing feelings of fullness and reduced food intake.
-
Weight loss following bariatric surgery can vary significantly from one individual to another. Results vary widely and depend on a number of factors, including a person’s starting weight and progress with lifestyle changes.
On average, individuals who undergo a sleeve gastrectomy lose around 25-35% of their initial body weight one year after their surgery.
-
All types of weight loss surgery are major operations and carry risks. Your surgeon will talk to you in detail about the risks of surgery.
Some of the risks of the sleeve gastrectomy include:
bleeding
infection
leakage from the staple line
scarring causing strictures
nutrient deficiencies
gastro-oesophageal reflux
weight loss not in line with expectations
Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
With this operation, a small pouch is created at the top of the stomach, and a portion of the small intestine is bypassed. This restricts the amount of food a person can eat and reduces nutrient absorption.
-
Weight loss following bariatric surgery can vary significantly from one individual to another. Results vary widely and depend on a number of factors, including a person’s starting weight and progress with lifestyle changes.
On average, individuals who undergo a Roux-en-Y gastric bypass lose around 30-35% of their initial body weight one year after their surgery.
-
All types of weight loss surgery are major operations and carry risks. Your surgeon will talk to you in detail about the risks of surgery.
Some of the risks of the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass surgery include:
bleeding
infection
vitamin and micronutrient deficiencies
bowel leak through surgical joins
dumping syndrome (the stomach cannot regulate food entering the small intestine, so large meals flood the intestine causing dizziness, abdominal pain, nausea and diarrhoea)
stenosis (narrowing) of the joins
bowel obstruction from internal hernias
ulcers
persistent constipation or diarrhoea
weight loss not in line with expectations
Who is eligible for weight loss surgery?
Eligibility for weight loss surgery is determined after a careful medical evaluation.
-
Weight loss surgery is generally considered for individuals who have a BMI of 40 or higher. It may also be considered for those with a BMI of 35 or higher who have significant obesity-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnoea.
-
Patients are required to have made significant attempts to lose weight through non-surgical methods such as diet and exercise.
-
Patients should be willing to make substantial changes to their diet and exercise habits before and after surgery.
Weight loss surgery is only a tool, and long term success requires lifestyle modifications.
In general, candidates for surgery often meet the following criteria:
What does BMI mean?
BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It's a numerical value of a person's weight in relation to their height, and is used as a tool to categorise people into different weight categories.
You can find out your own BMI using the Health New Zealand – Te Whatu Ora BMI Calculator.
BMI Categories
< 18.5
Underweight
Healthy Weight
18.5—24.9
Overweight
25—29.9
30—34.9
Obesity (Class 1)
35—39.9
Obesity (Class 2)
Obesity (Class 3)
> 40
BMI only provides a rough estimate of a person's body fat and helps healthcare professionals and researchers assess potential health risks associated with being underweight, overweight, or obese. However, it's important to note that BMI has limitations and doesn't take into account factors like muscle mass, bone density, and distribution of fat, so it may not be a perfect indicator of an individual's overall health. Therefore, it's often used in conjunction with other health assessments for a more comprehensive evaluation.
Weight Loss Surgery FAQs
-
Obesity is a chronic disease caused by a combination of our genes and the environment we live in. Like other diseases, it requires proactive measures for effective management.
-
Obesity can increase the risk of health complications. It is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke and certain cancers.
Obesity can also impact on chronic conditions such as sleep apnoea, osteoarthritis, high blood pressure and metabolic syndrome.
Treating obesity can help to reduce these risks and can assist in managing some chronic conditions.
-
Weight loss surgery is only one component in the management of obesity. It requires lifelong lifestyle changes and follow up, including annual blood tests. Your GP will need to be involved with your care following weight loss surgery.
In addition to this, we need an accurate record of your medical history before surgery.
For these reasons, we require a referral from your GP for weight loss surgery.
-
You will need to commence a strict VLCD (Very Low Calorie Diet) for at least 2 weeks (some patients may require longer) before surgery.
This diet involves replacing all meals with three VLCD products (e.g. Optifast®) and 2 cups of low starch vegetables per day.
The purpose of this diet is to reduce the size of the liver, making surgery safer.
Read more about the Pre-Bariatric Surgery Optifast® Diet here (PDF).
-
After your operation, you will be on a liquid diet.
You will remain on a liquid diet for the first 2 weeks following surgery, then a pureed diet for the next 2 weeks. After 4 weeks, you will be able to commence soft food. By 6 weeks, you should be able to commence a normal healthy diet.
-
Following surgery, you will require the following medications:
Multivitamins. These are important, and need to be taken daily for the rest of your life.
Antacid. You will be prescribed an antacid (Omeprazole) to take daily for one month following surgery. Some patients may need to take this longer to control heartburn symptoms.
Pain relief. You will be sent home with a prescription for pain relief tablets following surgery – these only need to be taken for a few days following surgery, and only if needed.
-
You will have follow up for up to 2 years after your operation by your surgeon and your dietitian.
After this period, you will be discharged back to the care of your GP.
You will need to have a blood test once per year for the rest of your life.
-
Most patients will require between 1 and 2 nights in hospital after surgery. If there are any complications following surgery, you may need more time in hospital.
-
We recommend planning for 2 weeks off work to recover from your operation.
Following this, you will be able to gradually return to work but we would recommend you do not perform heavy duties for at least 6 weeks.
If there are any complications from surgery, you might need more time off work.
-
We don’t perform the Gastric Banding procedure (sometimes called “Lap Band” or “Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding”).
This operation is not commonly performed anymore because the other operations we offer for the management of obesity have better long term results and lower rates of complications and revisions.
We do remove lap bands for patients if required.
-
You can read more about weight loss surgery on the Healthify webpage.
-
The Bariatric Surgery Registry (BSR) is a clinical quality registry which seeks to monitor the safety and efficacy of bariatric surgery across New Zealand and Australia.
Data will be collected about your operation and health.
Enrolment in the study is automatic, but is completely voluntary and you are entitled to opt out at any stage.
You will be given more information about the BSR during your consultation. You can also read more about the BSR on the official website, and can contact them by email at bsr@auckland.ac.nz or by phone on 0800 656 276.